Information about Diamonds, News
What are Black Diamonds and Carbonados?
Ever wondered about the alluring charm of black diamonds? These mysterious gems, often linked with elegance and sophistication, have a fascinating tale to tell. While most black diamonds available today are enhanced, it’s worth noting that natural black diamonds, though exceedingly rare, do exist. Additionally, there’s another intriguing type of diamond called carbonados, which is even more exceptional. In this article, we’ll delve into the realm of black diamonds and carbonados, unveiling their origins, unique colors, and distinct properties. Whether you’re a gem aficionado or simply curious about these enigmatic stones, this article, brought to you by Melogems, will provide the answers you’re looking for.

What are Black Diamonds?
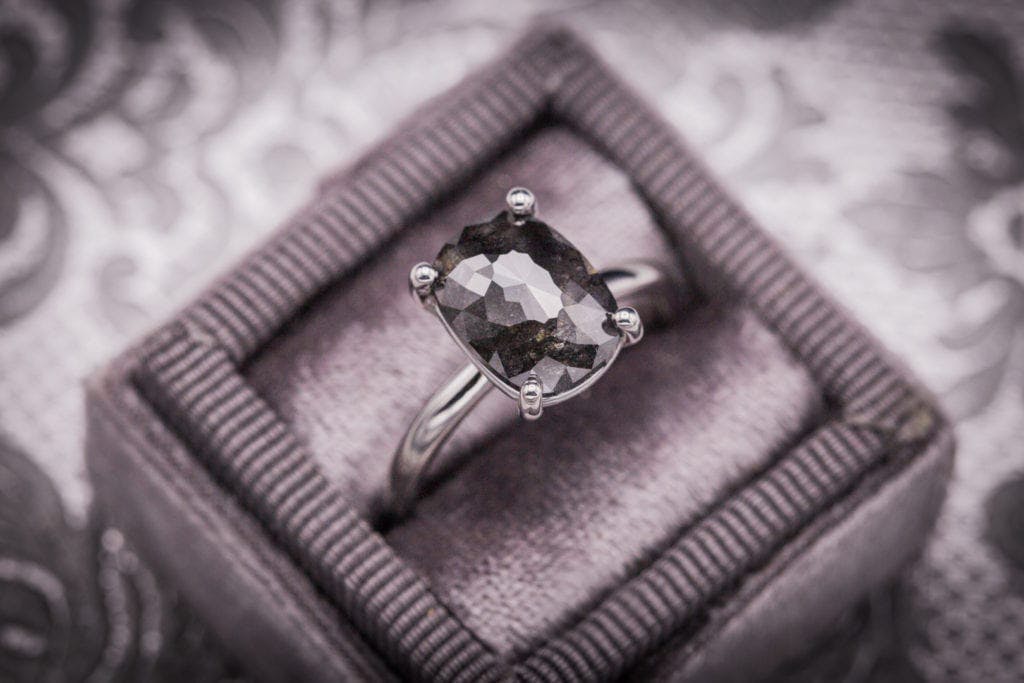
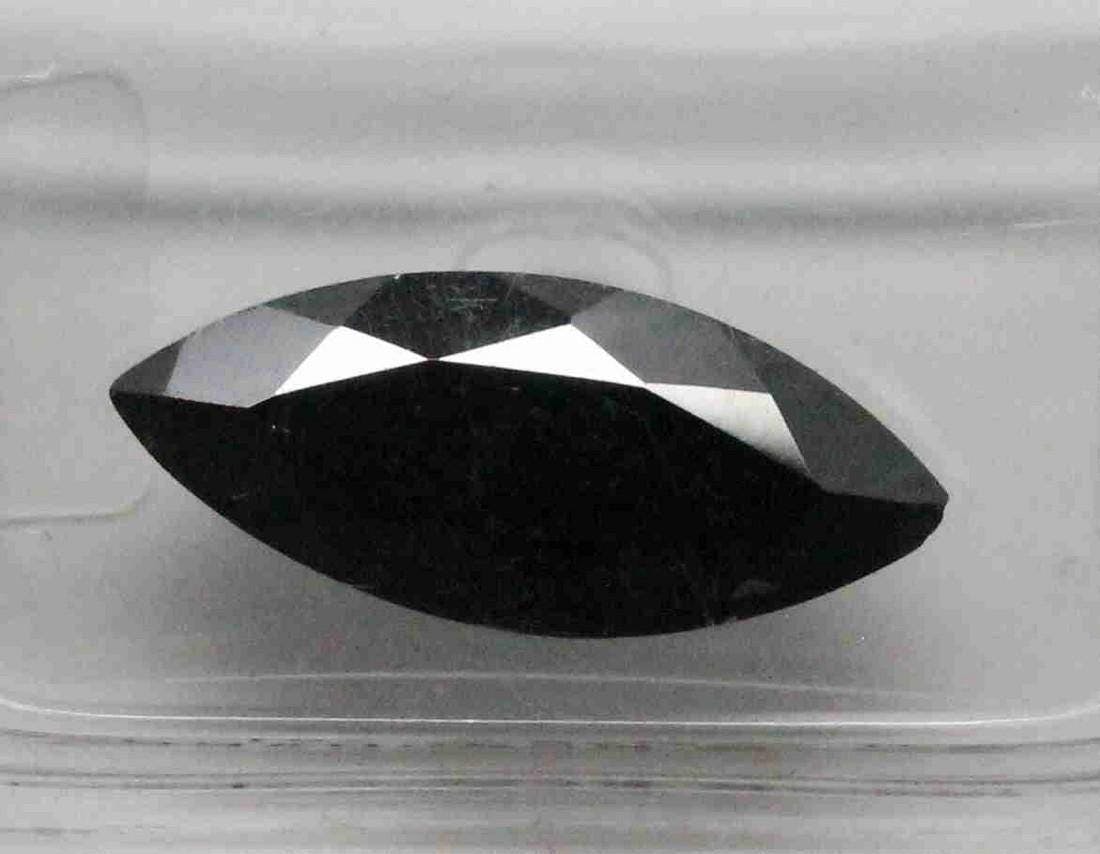
Black diamonds are a type of fancy colored diamonds that are graded and priced differently from the more common white or colorless diamonds. They are known for their dramatic and unique appearance, making them increasingly popular in recent years.
Black diamonds as fancy colored diamonds
Unlike white diamonds, black diamonds fall into the category of fancy colored diamonds. These diamonds have a distinct and intense color, which is caused by the presence of certain impurities and structural defects. While black diamonds may cost less than white diamonds due to a lack of consumer demand, their popularity has been on the rise.
Grading and cost of black diamonds
Black diamonds are graded based on their color, clarity, cut, and carat weight, just like any other diamond. However, the grading scale for black diamonds is different from that of white diamonds. The color of a black diamond is graded on a scale from Fancy Light to Fancy Black. The clarity of a black diamond is also different, as it is usually more included compared to white diamonds. The cost of a black diamond is determined by these factors, as well as its size and overall quality.
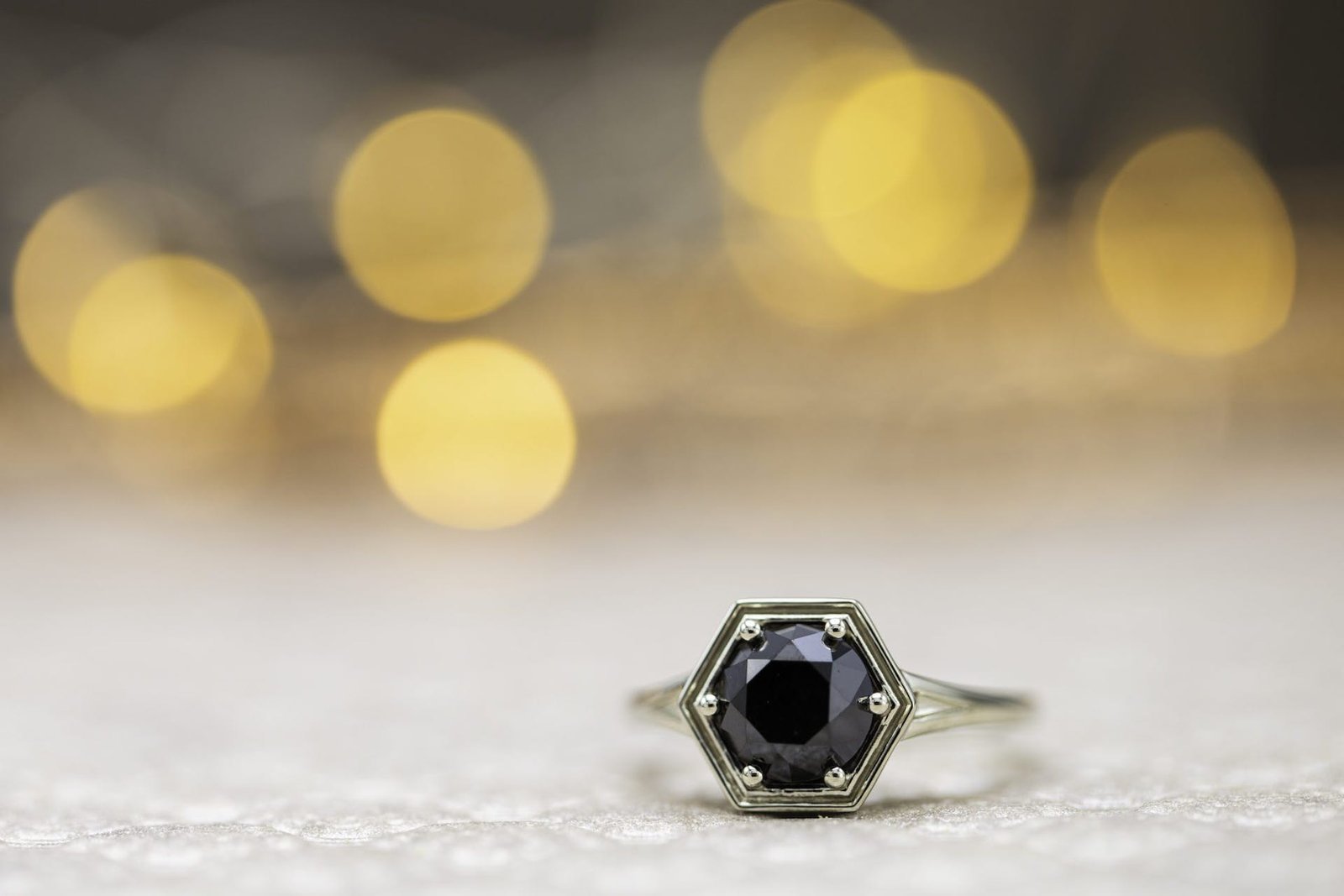
Increasing popularity of black diamonds
In recent years, black diamonds have gained popularity among those looking for something unique and different in their jewelry. Their striking appearance and unconventional color make them stand out from traditional white diamonds. Black diamonds are often used in engagement rings, statement earrings, and other types of jewelry. Their increasing popularity can be attributed to a growing appreciation for alternative gemstones and a desire for personalized and distinctive pieces.
How Do Black Diamonds Get Their Color?
The natural color of black diamonds comes from the presence of inclusions and fractures within the diamond. These small, dark-colored inclusions and fractures give black diamonds their characteristic black color. Most black diamonds are opaque, meaning they do not transmit light, and they have an almost metallic luster. Some black diamonds may also have a translucent appearance, resembling a “salt-and-pepper” effect.
Additionally, black diamonds may exhibit different colors when viewed from the side. While they appear black when viewed face-up, they may have a dark brown or dark green body color when viewed from certain angles.
Black diamonds can also be enhanced to achieve a darker and more uniform black color. These procedures include high pressure/high temperature (HPHT) treatments and radiation treatments. However, whether color treated or natural, the defining characteristics of a black diamond are its chemical composition (carbon with minor impurities) and its crystalline atomic structure.
Examples of natural black diamonds include the famous 67.5 carat “Black Orlov” and a 1.64 carat round black diamond treated with HPHT.
What are Carbonados?
Carbonados, often referred to as “black diamonds,” are an unusual type of diamond material. They are more accurately described as polycrystalline or aggregate diamond material composed of amorphous carbon, graphite, and diamond. Carbonados are known for their greater durability compared to crystalline diamonds and are primarily used in industrial applications.
Description of carbonados
Carbonados resemble charcoal in appearance, which is reflected in their name, as “carbonado” means “burned” in Portuguese. They have a distinct texture and color, often appearing rough and porous. Carbonados are typically black or dark gray in color, with a rough, matte surface.
Use of carbonados in industry
Due to their unique composition and durability, carbonados are used in various industrial applications. They are commonly used in drilling and cutting tools, as well as in grinding and polishing equipment. The toughness of carbonados makes them well-suited for these applications, as they can withstand high pressure and abrasive conditions.
Explore More: Ruby with Diamond Ring at Melogems!
Sale of faceted carbonado diamond
While carbonados are primarily used in industry, there have been instances where faceted carbonado diamonds have been sold. In February 2022, Sotheby’s auctioned a faceted carbonado diamond named “Enigma,” weighing 555.55 carats. This sale demonstrates the growing interest in unusual and rare gemstones among collectors and enthusiasts.
Similarities to charcoal
Carbonados share some similarities with charcoal, both in appearance and composition. They are often compared to charcoal due to their black color, rough texture, and matte surface. The name “carbonado” further emphasizes this similarity, as it means “burned” in Portuguese. However, carbonados are much harder and more durable than charcoal, making them suitable for industrial use.
Origin theories of carbonados
The origin of carbonados is still a subject of debate among scientists and researchers. One theory suggests that carbonados originated from extraterrestrial sources, such as meteorites. The presence of nitrogen, hydrogen, and osbornite (a mineral found only in meteors) in carbonados supports this theory. It is believed that carbonados formed in outer space and later reached Earth through natural processes.
Another theory proposes that carbonados were formed during supernova explosions. According to this theory, chunks of carbonado material were sent into space during these explosive events and eventually collided with Earth. This could explain the unique properties and distribution of carbonados, as they would have already been formed when they arrived on Earth.
An Extraterrestrial Material?
Carbonados have certain characteristics that suggest an extraterrestrial origin. Unlike crystalline diamonds, which are typically found in igneous kimberlite rock formed deep within the Earth, carbonados occur in alluvial and sedimentary deposits. These deposits are more commonly associated with materials that have been transported from outer space.
Furthermore, the micro-diamonds within carbonados lack the minerals typically found in the Earth’s mantle, indicating a different formation process. Traces of nitrogen, hydrogen, and osbornite, which are not commonly found in diamonds, further support the extraterrestrial origin theory for carbonados.
While more research is needed to confirm these theories, the possibility of carbonados originating from outer space adds to their allure and intrigue.
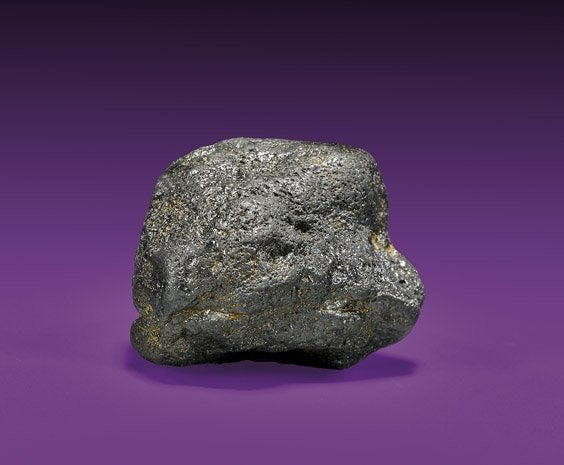

Carbonado Sources
Carbonados are believed to have formed between 2.6 and 3.8 billion years ago, during a specific period in Earth’s history. They are primarily found in Brazil and the Central African Republic, suggesting a limited occurrence. The geological history of these regions offers insights into the formation and distribution of carbonados.
During the time when carbonados were formed, present-day Brazil and the western coast of Africa may have been part of a “supercontinent,” preceding the well-known Gondwanaland. This supercontinent stage may have played a role in the formation of carbonados, possibly through a diamond meteorite impact.
These unique geological conditions and specific time period could explain why carbonados are found only in certain regions and provide valuable clues to their origin.
Diamonds from a Supernova?
One proposed theory for the origin of carbonados suggests that they were formed during supernova explosions. According to researchers Jozsef Garai and Stephen Haggerty, carbonados may have been created through the extreme conditions and pressures generated during these explosive events.
During a supernova explosion, massive stars reach the end of their lives and undergo a catastrophic collapse. This collapse releases an enormous amount of energy, causing the star to explode. The intense heat and pressure generated during the explosion could have transformed carbon-rich materials into polycrystalline diamond structures, resulting in the formation of carbonados.
After their formation in supernovae, the chunks of carbonados would have been propelled into space and eventually found their way to Earth. This theory provides an alternative explanation for the unique properties of carbonados and their extraterrestrial-like characteristics.
The study of carbonados and their possible connection to supernovae offers a fascinating glimpse into the cosmic origins of these extraordinary diamonds.
Explore Emerald Gemstone in Singapore at Melogems!