Information about Diamonds, Information about Garnets, Information about Gemstone Necklaces, Information about Jade, Information about Ruby, Information about Sapphire, Information about Zircon, News
Synthetic Gemstone Guide: Science, Identification, and Valuation
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of synthetic gemstones with the Synthetic Gemstone Guide from Melogems—a comprehensive resource that delves into the science, identification, and valuation of synthetic gems. This guide covers everything you need to know, from the intricate manufacturing processes behind popular gemstones like rubies, sapphires, emeralds, and opals, to insights on gemstone jewelry settings, metals, tools, and cutting techniques.
Whether you’re a passionate gemstone enthusiast, a seasoned jeweler, or simply curious about the world of synthetic gems, this guide stands as your go-to source for in-depth information and expert advice. The Synthetic Gemstone Guide features an extensive Gemstone Encyclopedia, a captivating Gem Photo Gallery, and a valuable Gem Pricing section—providing you with all the essential tools to explore, learn, and appreciate the beauty and worth of synthetic gemstones.
Science of Synthetic Gemstones
Introduction to Synthetic Gemstones
In the world of gemstones, there is a fascinating category known as synthetic gemstones. Synthetic gemstones are lab-created gemstones that possess the same chemical composition and physical properties as their natural counterparts. These gems are created through advanced manufacturing processes, utilizing a combination of science and technology to produce stunning gemstones that are highly sought after in the jewelry industry.
Manufacturing Processes of Synthetic Gemstones
The manufacturing processes of synthetic gemstones can vary depending on the type of gemstone being created. However, there are a few common methods used in the production of these gems. One such method is the flux-growth process, which involves melting various compounds together to form a crystal. Another popular method is the hydrothermal process, where the gemstone is grown in a high-pressure, high-temperature environment.
Properties of Synthetic Gemstones
Synthetic gemstones possess the same chemical and physical properties as their natural counterparts. This means that they have the same hardness, luster, and refractive index as natural gemstones. However, there are some subtle differences that can be detected upon careful examination. For example, synthetic gemstones may have growth lines or inclusions that are not typically found in natural gemstones.
Comparison to Natural Gemstones
When it comes to the comparison between synthetic and natural gemstones, there are a few key differences to consider. While synthetic gemstones can closely mimic the appearance of natural gemstones, they are generally more affordable and readily available. Additionally, synthetic gemstones are often free from the ethical concerns associated with the mining of natural gemstones. However, some collectors and enthusiasts may still prefer the rarity and uniqueness of natural gemstones.

Identification of Synthetic Gemstones
Physical Characteristics of Synthetic Gemstones
Identifying synthetic gemstones can be a fascinating and intricate process. One of the first things to look for is the physical characteristics of the gemstone. Synthetic gemstones may exhibit certain traits that are not commonly seen in their natural counterparts. These characteristics can include unusually perfect clarity, consistent color distribution, and lack of natural imperfections.
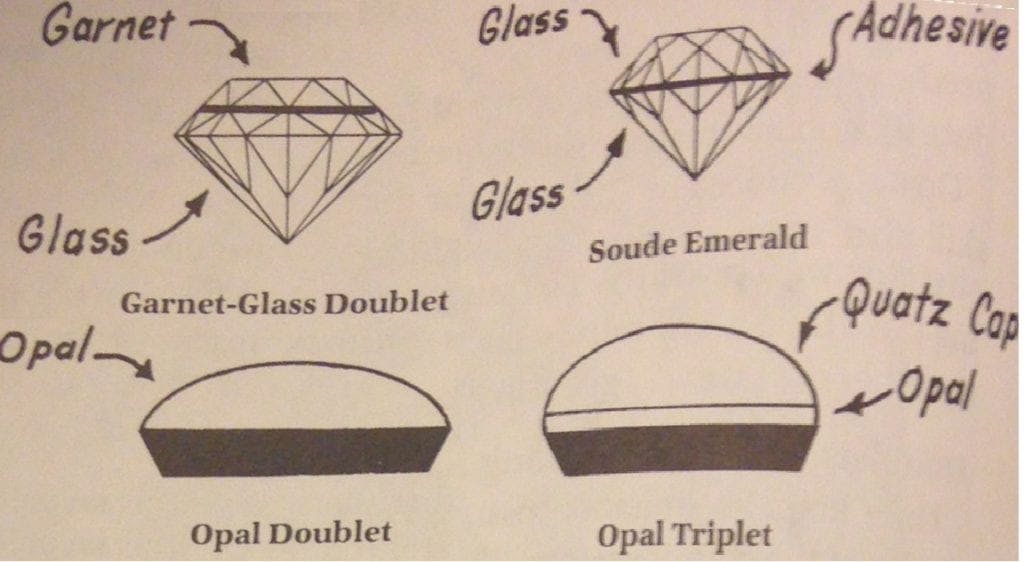
Inclusions and Growth Lines in Synthetic Gemstones
Inclusions and growth lines are another important aspect to consider when identifying synthetic gemstones. These features can provide valuable clues about the origin of the gemstone. While natural gemstones often have a unique pattern of inclusions and growth lines, synthetic gemstones may exhibit more uniform and predictable patterns.
Tools and Techniques for Identification
The identification of synthetic gemstones requires specialized tools and techniques. Gemologists and trained professionals often use a combination of magnification tools, such as microscopes and loupes, to examine the gemstone closely. Additionally, they may utilize various spectroscopic techniques to analyze the gemstone’s chemical composition.
Identification Challenges
Identifying synthetic gemstones can be challenging, as manufacturers continue to improve their production processes to make the gems more natural-looking. However, advancements in gemological technology and the expertise of gemologists allow for accurate identification. It is important to stay updated on the latest techniques and developments in the field to ensure accurate identification of synthetic gemstones.

Valuation of Synthetic Gemstones
Factors Affecting the Value of Synthetic Gemstones
Various factors can affect the value of synthetic gemstones. These factors include the size, color, clarity, and overall quality of the gemstone. Additionally, market demand and trends can also play a significant role in determining the value of synthetic gemstones.
Pricing Guidelines for Synthetic Gemstones
Pricing synthetic gemstones can be different from pricing natural gemstones. Due to their abundance and ease of production, synthetic gemstones are generally priced lower than their natural counterparts. However, the value of synthetic gemstones can still vary based on factors such as the gemstone’s quality, rarity, and desirability.
Market Demand and Trends
The market demand for synthetic gemstones has been steadily increasing over the years. As consumers become more aware of the benefits and affordability of synthetic gemstones, the demand for these gems continues to rise. Additionally, current trends in the jewelry industry, such as sustainable and ethical jewelry, have also contributed to the growing popularity of synthetic gemstones.
Appraisal and Certification of Synthetic Gemstones
Appraisal and certification of synthetic gemstones are important steps in the gemstone industry. Certified gemologists can provide accurate and detailed information about the gemstone’s origin, quality, and value. This certification process adds credibility and transparency to the sale and purchase of synthetic gemstones.
Types of Synthetic Gemstones
Synthetic Ruby
Synthetic ruby is one of the most well-known and popular types of synthetic gemstones. It is created by melting aluminum oxide with traces of chromium, resulting in crystals with the same properties as natural ruby. Synthetic rubies have been synthesized since the mid-19th century to meet the high demand for these stunning red gemstones.
Synthetic Sapphire
Synthetic sapphire is another widely recognized synthetic gemstone. It shares the same chemical composition and physical properties as natural sapphire. Synthetic sapphires have been produced since the mid-19th century and are highly valued for their brilliant blue color.
Synthetic Spinel
Synthetic spinel is a versatile gemstone that is commonly used to imitate other gemstones. It can be created using the Verneuil process, which involves melting various compounds together. Synthetic spinel is often used to imitate gemstones such as ruby, sapphire, and diamond.
Synthetic Quartz
Synthetic quartz is a popular choice for various applications, including gem quartz. It can be made in large quantities using different manufacturing processes. Synthetic quartz is highly valued for its clarity and durability, making it an excellent alternative to natural quartz.
Synthetic Emerald
Synthetic emerald has been produced since the early 20th century using various techniques such as hydrothermal and flux-growth. These lab-created emeralds possess the same stunning green color as their natural counterparts and are highly sought after in the jewelry industry.
Other Synthetic Gems
In addition to ruby, sapphire, spinel, quartz, and emerald, there are various other synthetic gemstones available in the market. These include opal, turquoise, lapis lazuli, and synthetic rutile. These synthetic gems offer a wide range of colors and characteristics, providing options for every jewelry enthusiast.
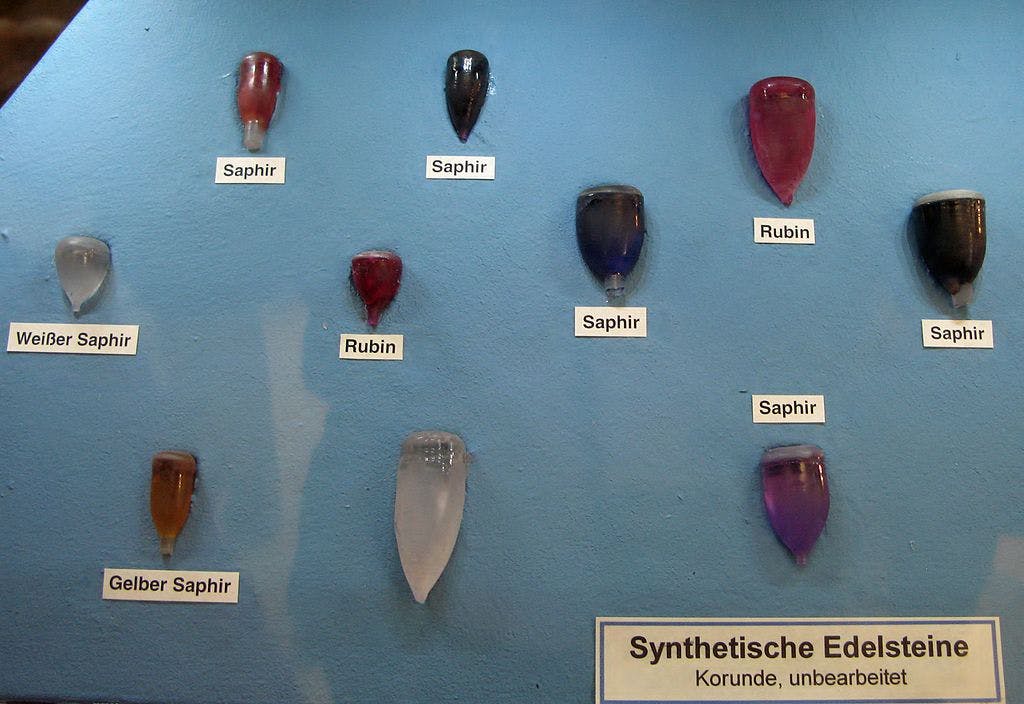

Synthetic Ruby
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Ruby
The manufacturing process of synthetic ruby involves melting aluminum oxide with traces of chromium. This mixture is then carefully cooled and crystallized to form synthetic ruby crystals. The crystals are then cut and polished to create beautiful gemstones.
Properties and Characteristics of Synthetic Ruby
Synthetic ruby shares the same properties and characteristics as natural ruby. It has a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest gemstones. Synthetic ruby also exhibits a rich red color and a brilliant luster, making it highly desirable in the jewelry industry.
Uses and Applications of Synthetic Ruby
Synthetic ruby is widely used in various applications, including jewelry and industrial purposes. In jewelry, synthetic ruby is often used as a more affordable alternative to natural ruby. It is commonly used in rings, necklaces, earrings, and other pieces of jewelry. In the industrial sector, synthetic ruby is used in lasers, watch bearings, and other specialized equipment.
Distinguishing Synthetic Ruby from Natural Ruby
Distinguishing synthetic ruby from natural ruby can be challenging, as synthetic ruby closely resembles its natural counterpart. However, there are certain characteristics that can help in identification. Synthetic rubies may exhibit characteristic growth lines or inclusions that are not commonly found in natural rubies. Additionally, gemological testing and analysis can provide further insight into the gemstone’s origin and composition.
Synthetic Sapphire
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Sapphire
The manufacturing process of synthetic sapphire involves the use of various techniques such as the Verneuil process and the Czochralski process. These processes involve melting aluminum oxide and carefully crystallizing it to form synthetic sapphire crystals. These crystals are then cut and polished to create stunning gemstones.
Properties and Characteristics of Synthetic Sapphire
Synthetic sapphire possesses the same properties and characteristics as natural sapphire. It has a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest gemstones. Synthetic sapphire exhibits a beautiful blue color and a high refractive index, resulting in exceptional brilliance and luster.
Uses and Applications of Synthetic Sapphire
Synthetic sapphire has a wide range of uses and applications. In the jewelry industry, synthetic sapphire is often used as a more affordable alternative to natural sapphire. It is commonly used in engagement rings, pendants, and earrings. Additionally, synthetic sapphire is highly valued in the watch industry, where it is used to create durable and scratch-resistant watch crystals.
Distinguishing Synthetic Sapphire from Natural Sapphire
Distinguishing synthetic sapphire from natural sapphire can be challenging, as the two can closely resemble each other. However, there are certain characteristics that can help in identification. Synthetic sapphire may exhibit characteristic growth lines or inclusions that are not typically found in natural sapphire. Additionally, advanced spectroscopic techniques can provide valuable insight into the gemstone’s composition and origin.

Synthetic Spinel
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Spinel
Synthetic spinel is commonly created using the Verneuil process, where various compounds are melted and crystallized to form spinel crystals. This process allows for the production of synthetic spinel that closely mimics its natural counterpart. The synthetic spinel crystals are then cut and polished to create beautiful gemstones.
Properties and Characteristics of Synthetic Spinel
Synthetic spinel possesses similar properties and characteristics to natural spinel. It has a hardness of 8 on the Mohs scale, making it a durable gemstone. Synthetic spinel exhibits a wide range of colors, from vibrant reds and blues to stunning purples and pinks.
Imitation of Other Gemstones with Synthetic Spinel
One of the unique characteristics of synthetic spinel is its ability to imitate other gemstones. Synthetic spinel can closely resemble gemstones such as ruby, sapphire, and diamond. This quality makes it a popular choice for those looking for affordable alternatives to these precious gemstones.
Distinguishing Synthetic Spinel from Natural Spinel
Distinguishing synthetic spinel from natural spinel can be challenging due to their similar properties. However, there are certain characteristics that can help in identification. Synthetic spinel may exhibit growth lines or inclusions that are not commonly found in natural spinel. Additionally, gemological testing and analysis can provide valuable information about the gemstone’s composition and origin.
Synthetic Quartz
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Quartz
Synthetic quartz is produced using various manufacturing processes, including the hydrothermal process and the flame fusion process. These processes involve creating a high-pressure, high-temperature environment to grow quartz crystals. The resulting synthetic quartz crystals are then cut and polished to create stunning gemstones.
Properties and Characteristics of Synthetic Quartz
Synthetic quartz possesses similar properties and characteristics to natural quartz. It has a hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale, making it a relatively hard gemstone. Synthetic quartz exhibits exceptional clarity and transparency, allowing light to pass through it beautifully.
Applications and Uses of Synthetic Quartz
Synthetic quartz has a wide range of applications and uses. In the jewelry industry, synthetic quartz is often used as an affordable alternative to natural quartz. It is commonly used in rings, pendants, and bracelets. Additionally, synthetic quartz is widely used in various industrial applications, such as oscillators, sensors, and microchips.
Distinguishing Synthetic Quartz from Natural Quartz
Distinguishing synthetic quartz from natural quartz can be challenging, as they share similar properties. However, there are certain characteristics that can help in identification. Synthetic quartz may exhibit growth lines or inclusions that are not typically found in natural quartz. Additionally, gemological testing and analysis can provide valuable information about the gemstone’s origin and composition.

Synthetic Emerald
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Emerald
Synthetic emerald is created using various manufacturing techniques, including the hydrothermal process and the flux-growth process. These processes involve creating a high-pressure, high-temperature environment to simulate the conditions in which natural emeralds are formed. The resulting synthetic emerald crystals are then cut and polished to create stunning gemstones.
Properties and Characteristics of Synthetic Emerald
Synthetic emerald shares similar properties and characteristics with natural emerald. It has a hardness of 7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale, making it a relatively hard gemstone. Synthetic emerald exhibits a vibrant green color and a high refractive index, resulting in exceptional brilliance and luster.
Uses and Applications of Synthetic Emerald
Synthetic emerald is widely used in the jewelry industry as an affordable alternative to natural emerald. It is commonly used in rings, necklaces, and earrings. Additionally, synthetic emerald is highly valued in the field of astrology and spiritual healing, where it is believed to possess various metaphysical properties.
Distinguishing Synthetic Emerald from Natural Emerald
Distinguishing synthetic emerald from natural emerald can be challenging, as synthetic emeralds closely resemble their natural counterparts. However, there are certain characteristics that can help in identification. Synthetic emeralds may exhibit growth lines or inclusions that are not typically found in natural emeralds. Additionally, advanced gemological testing and analysis can provide valuable information about the gemstone’s origin and composition.
In conclusion, synthetic gemstones have revolutionized the jewelry industry. With their stunning beauty and affordability, synthetic gemstones offer a viable alternative to natural gemstones. Through advanced manufacturing processes and cutting-edge technology, these lab-created gems possess the same chemical composition and physical properties as their natural counterparts. The identification and valuation of synthetic gemstones require specialized tools and expertise, but with advancements in gemological science, accurate identification is achievable. From synthetic ruby and sapphire to spinel, quartz, and emerald, the world of synthetic gemstones offers a wide range of options for jewelry enthusiasts. Whether it be for personal adornment, collection, or industrial applications, synthetic gemstones continue to captivate us with their allure and brilliance.