News
An Introduction to Gemology
Are you curious about the world of gemology and how gemstones are formed? Look no further than “An Introduction to Gemology.” In this article, you’ll learn about one of the most abundant minerals on Earth – quartz. Discover the different varieties of quartz and how they are cut by lapidaries to create stunning gemstone jewelry. Delve into the fascinating process of how quartz forms in igneous rocks or geothermal waters. Uncover the secrets behind the beautiful smoky brown shades of smoky quartz and the vibrant purple hues of amethyst. Whether you’re a gem enthusiast or simply interested in the intricate processes of the Earth, this article is the perfect introduction to the enchanting world of gemology.

Table of Contents
What is Quartz?
How Does Quartz Form?
How Does Smoky Quartz Form?
How Does Amethyst Form?
How Does Citrine Form?
How Does Ametrine Form?
How Does Rose Quartz Form?
How Does Chalcedony Form?
Related Articles
More Articles
What is Quartz?
Quartz is one of the most abundant minerals on Earth. It is a crystalline form of silicon dioxide and comes in many different varieties. Some popular gem forms of quartz include amethyst, citrine, and agate. When quartz grows into large crystals, lapidaries can cut varieties such as rock crystal, smoky quartz, amethyst, or citrine. Quartz can also form into stones made of tiny microcrystals, which lapidaries can cut into chalcedonies like agate or jasper.
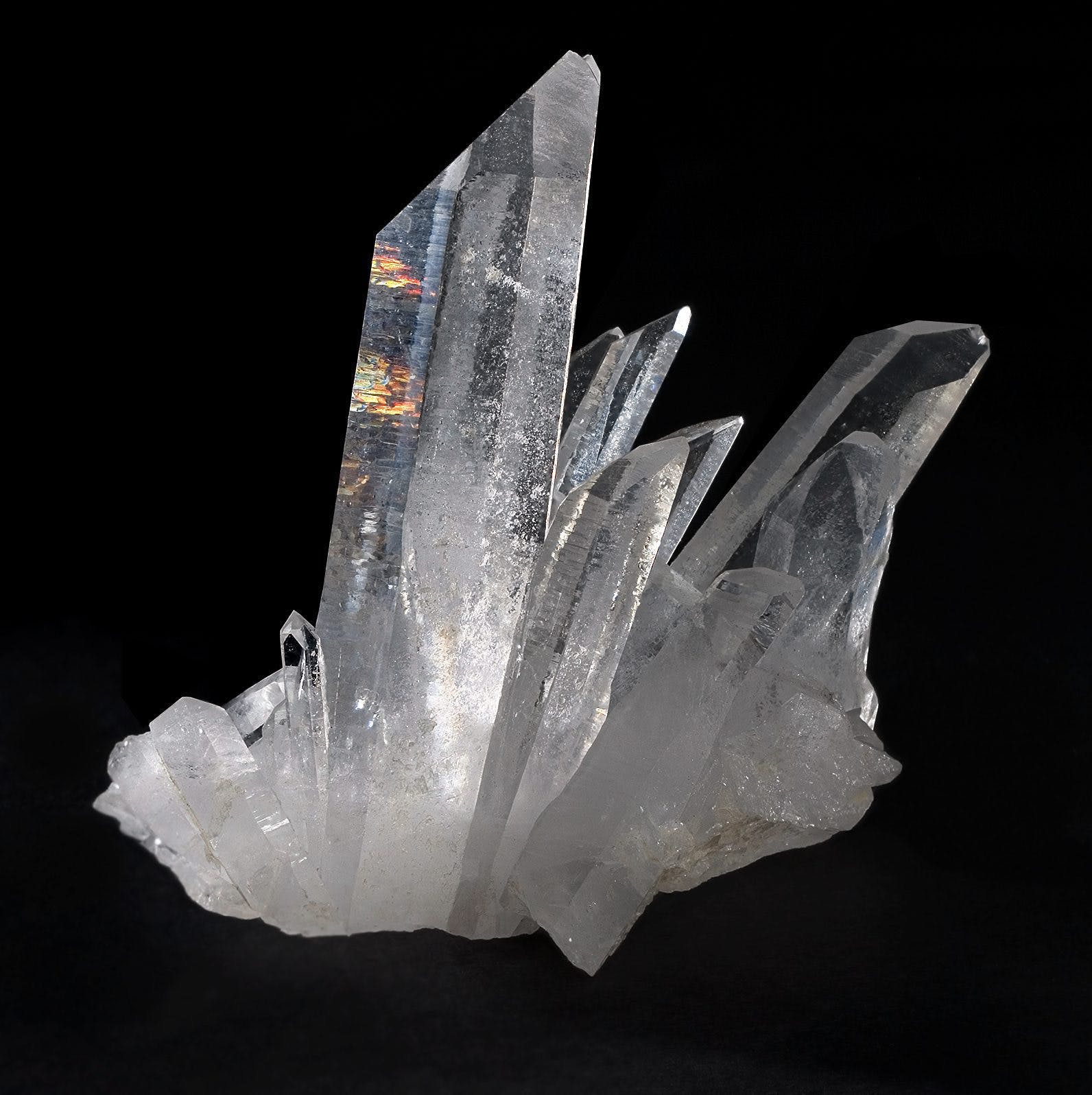
How Does Quartz Form?
Quartz can form in two main ways: in igneous rocks or in environments with geothermal waters. In igneous rocks, quartz forms as magma cools. Just like water turning into ice, silicon dioxide crystallizes as it cools. Slow cooling allows the crystals to grow larger. Quartz can also form from silica-rich water in a similar manner. Silicon dioxide dissolves in water at high temperature and pressure, and when the temperature or pressure drops, the solution becomes saturated, leading to quartz crystal formation.
How Does Smoky Quartz Form?
Smoky quartz gets its characteristic smoky brown shades when the rocks surrounding it contain radioactive elements. Over time, the radiation alters the crystal structure of quartz, causing defects and creating the smoky color. The intensity of the color can vary depending on the amount of radiation exposure and the concentration of the radioactive elements in the surrounding rocks.

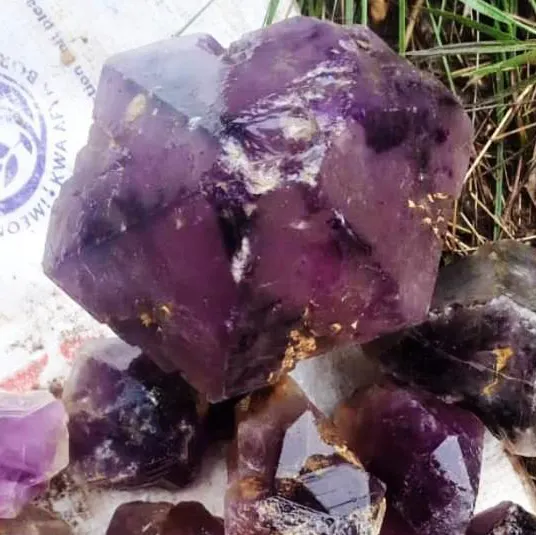
How Does Amethyst Form?
Amethyst is a variety of quartz that displays a purple color. It forms when silicon dioxide crystals are exposed to specific conditions during their growth. The presence of iron impurities within the crystal lattice of quartz gives amethyst its distinct purple hue. The intensity of the purple color can vary and is often influenced by factors such as the concentration of iron impurities and the duration of exposure to the specific conditions required for amethyst formation.
How Does Citrine Form?
Citrine is a variety of quartz that exhibits yellow to orange colors. It forms when silicon dioxide crystals undergo heat treatment. Natural citrine is relatively rare, and most of the citrine on the market today is produced by heat treating amethyst or smoky quartz. The heat treatment removes any impurities that could distort the yellow color of citrine, resulting in a vibrant and uniform hue.

How Does Ametrine Form?
Ametrine is a unique gemstone that combines the colors of both amethyst and citrine. It forms when a quartz crystal contains zones of both purple amethyst and yellow citrine. The color zoning in ametrine is a result of temperature fluctuations during the crystal’s growth. The exact process of ametrine formation is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a natural occurrence rather than a result of human intervention.
How Does Rose Quartz Form?
Rose quartz is a variety of quartz that displays a pale pink color. The pink hue is caused by traces of titanium, iron, or manganese within the quartz crystal lattice. These impurities give rose quartz its delicate and soft appearance. While the exact process of rose quartz formation is not fully understood, it is believed to occur when silicon dioxide crystals are exposed to specific conditions that allow the incorporation of these impurities.

How Does Chalcedony Form?
Chalcedony is a cryptocrystalline variety of quartz that consists of very small crystals. It can occur in a variety of colors and is commonly used in the creation of gemstones such as agate and jasper. Chalcedony forms when silicon dioxide dissolves in water and then precipitates into tiny crystals within cavities or fractures in rocks. Over time, these crystals grow and fuse together, creating the dense and colorful chalcedony formations commonly seen in jewelry.
Related Articles
- Quartz Value, Price, and Jewelry Information
- What is Gemstone Luminescence?
- Top Spots for Gem Hunting in the US
- Trapiche Gems: An Introduction

More Articles
- 16 Famous Opals and Their Amazing Stories
- Verdelite (Green Tourmaline) Buying Guide
- Vanadinite Value, Price, and Jewelry Information
- Price and Value: Factory-Cut vs Custom-Cut Gemstones
In conclusion, quartz is a versatile and abundant mineral that can form in various ways depending on its surroundings. From the rich purple hues of amethyst to the vibrant yellows of citrine, each variety of quartz has its own unique formation process. Understanding how quartz forms can enhance your appreciation for these beautiful gemstones and their natural origins.